Introduction
Saliva is a complex biological fluid secreted by acinar cells of the major and minor salivary glands. It is an indicator of various plasma constituents.1 It is an important discriminating element in forensic biology, act as an indicator of salivary gland conditions, toxicological and drug monitoring.2 Thiocyanate concentration in saliva can be analyzed by gas spectrometry. It is an important parameter in classifying patients as smokers and nonsmokers, determination of certain clinical conditions and in forensic drug testing.3 Extracellular nucleic acids serve as cancer biomarkers and are detectable in a variety of biological fluids including breast milk, semen, saliva, urine, plasma as well as supernatants in cell cultures,4 Therefore, an improved collection method is required first to identify the invisible saliva stains on human skin and then proceed with other methods of extracting DNA to identify the suspect and exclude the innocent.5 Statherin and Histatin 3 are the indicators used for salivary detection.6 Various chemicals like enzymes and salts have also been tried out to detect dried saliva stains. Most commonly used enzymes are alkaline phosphatase, starch and amylase.7, 8, 9 Unfortunately, there are limitations of each test; alkaline phosphatase is not very specific as it gives a false-positive result. Starch or iodine test for amylase has been used for many years,.
Significant amount of saliva is deposited on the skin during biting, sucking, licking or kissing, and possibly through other behaviour.10, 11 It can act as an important source in forensic evidence. In human’s saliva is composed of 99.5% of water, 0.5 % consists of electrolytes, WBCs, epithelial cells, enzymes, lysozymes, and mucus and antimicrobial agents.12 In forensic cases of sexual assault and child abuse, bite marks analysis is very difficult because human dentition does not always leave identifying features imprinted on the skin surface.13 Detection of saliva stains encountered in forensic science casework is one of the primary objectives for forensic serologist as saliva is an important source of DNA.14 Detection of saliva from human skin can be an important source for identifying an individual.15 Unfortunately dried saliva stains are invisible to the human eye which adds to difficulty in recognizing and collecting. There are so many body fluids which has been used since years. Blood is being used as main investigatory tool because of its specific color. Rapid detection and visualization of human saliva stain is one of the challenging tasks in forensic cases, such as murder, rape, sexual assault, and child abuse. A more challenging question is to detect dry saliva stains from certain difficult surfaces eg. kitchen paper towels, fabrics cloths, stainless steel spoon,( cutlery) plastic glass, paper glass because these items surfaces are considered as absorptive textured and fragile materials, rendering saliva either to be evaporated or soaked quickly. In the present study saliva stains on different fabrics viz. silk, polyester, linen, jute, cotton, georgette, sarton and other items like paper cups, chocolate wrapper aluminium, plastic bags, stainless steel spoon (cutlery) were examined using Lugol’s iodine. Lugol’s Iodine test was found to give Positive results for saliva stains on different fabrics and it was also found that the stains on different fabrics gives positive results for saliva even after washing with water, but none of the fabrics gave positive results for saliva after washing with detergents and alcohol. The ability of a fabric to retain stains of saliva after washing depends not only upon the chemistry and manufacturing of the fabrics but also upon the time of immersion of the fabric with water and detergent and also the method adapted to remove the stain from the fabrics. It is thus concluded that the enzyme present in saliva stick/adhere the fabrics which is generally not removed even after immersing in water and gives positive results whereas the use of detergents on different fabrics removes the stains completely and fails to give result for saliva stains and as the use of alcohol on different fabrics darkens the stains.
Materials and Methods
Material needed
Lugol’Iodine – (5%) This is main reagent of our study
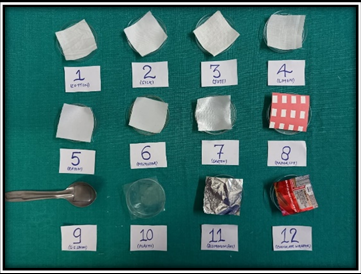
Fabrics: silk, cotton, linen, jute, polyester, rayon, satin
Every items put in different patri dishes. Investigator has collected her unstimulated saliva (10ml) by spitting method in a clean sterile container. All the study items has been stained with saliva and allowed to dry at room temperature by placing in numbered Petri dishes. We have made four groups on the basis of different activities.
Group A: the study items were subjected to 0.5ml of Lugol’s iodine solution after a period of 12 hours, 24 hrs, 48 hrs and after 7 days.
After washing with alcohol, saliva stains has been completely removed, but Lugol’s Iodine colour became darker in fabric due to iodoform reaction occur. (When alcohol react with Lugol’s Iodine give iodoform reaction). Amylase is an enzyme that breaks down starch into sugars. In amylose, sugar molecule form a structure that has small spaces in between the molecule of sugar.
Table 1
Visible color changes after application ofLugol’s iodine (+: Present;-: Absent)
Figure 3
Group A1: Study items subjected to 0.5 ml of Lugol’s iodine solution after a period of 12 hours and colour change is noted.

Figure 4
Group A: Study items subjected to 0.5 ml of Lugol’s iodine solution after a period of 24 hours.
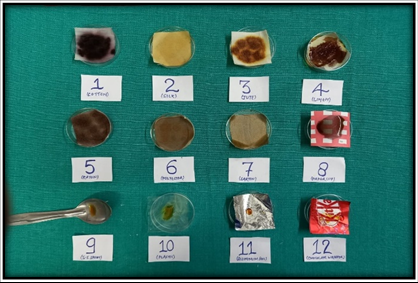
Figure 5
Group A3: Study items subjected to 0.5 ml of Lugol’s iodine solution after a period of 48 hours and colour change is noted.

Figure 6
Group A4: Study items subjected to 0.5 ml of lugol’s iodine solution after a period of 7 days and colour change is noted.

Figure 7
Group B: Study items washed thoroughly with distilled water allowed to dry at room temperature& then subjected to Lugol’s iodine and colour change is noted.
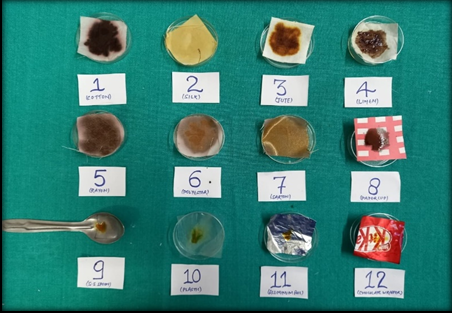
Figure 8
Group C: Study items washed thoroughly with alcohol allowed to dry at room temperature and subjected to Lugol’s iodine solution and colour change is noted.

Figure 9
Group D: Study items washed thoroughly with detergents (1 gm of commercially available detergents Tide to be mixed in 500 ml of water) allowed to dry at room temperature & then subjected to Lugol’s iodine solution and colour change is noted.

Lugol’s Iodine solution contains iodine molecules that fit tightly inside these small spaces When the iodine molecules are inside these small spaces between bonded sugar molecules, iodine looks blue black in colour. If the sugar molecules begin to break apart and release the Iodine molecules, the indicator solution looks light brown to brown in colour. Saliva is one of the important body fluids in criminal investigation. Presence of amylase is detected by using Lugol’s Iodine solution on different items. It can be detect even after washing with water. Different colour is obtained because of different webbing capacity of different clothes. Many information can be gathered in crime scene investigation through saliva examination. Saliva is generally found in sexual assault cases, or gags (cloths used to tie in mouth) in kidnapping cases or other sexually abuse cases.
Conclusion
Saliva is very important body fluid in criminal investigation. It is very difficult to detect because of its transparent colour. Many information can be gathered through saliva examination. From the study it is concluded that the saliva is retained in fabrics even after washing with water, due to enzymes present in saliva stick the fabrics which is generally not removed with washing with water. But after washing with detergents, It is completely removed but after washing with alcohol it becomes darkens in colour. If the criminal attempts to eliminate saliva from fabrics and different items from the crime scene. It can be still deteedct by using Lugol’s iodine.