Introduction
“Beauty lies in the eye of the beholder” is the universally recognized truth regarding physical attractiveness. Various factors through multiple explorations in the field of facial perception have been identified. There is no single principle which can define beauty.1 Rhodes2 identified and focused on factors & their links to attractiveness. Little et al.3 found that one’s perception of own attractiveness determines the opinion of others’ attractiveness, thereby DeBruine4 confirmed that faces resembling their own have been preferred by both sexes.
Not only the architectural structures, the musical composition as well as the dimensions of the human body demonstrate the golden section and the golden rectangle, a figure which is spanned by two sides in the golden section ratio.5, 6 Moreover, the golden section is effectively applied in line, the length is divided into two sub segments: a major sub segment and a minor sub segment.7 In this paper, we have taken a call to standardize protocols for regarding Golden proportion in facial profile analysis.
The golden section
The composition of golden section has fascinated mathematicians & artists since time immemorial.
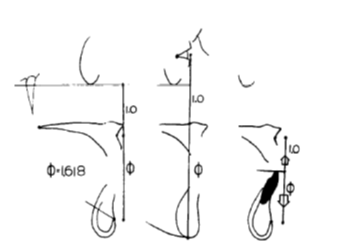
To present golden section geometrically, a line segment with length L is divided into sub segment – a major & a minor. M depicting major segment while m depicting minor segment.
Therefore it is to say that the geometric mean of L & m is M. Euclides (4th century BC), M2 is the spanned by the major, is equivalent to the Lm, which in turn is the area spanned by the length L & the minor m. Φ derived from the name of Greek sculptor Phidias (5th century BC), is used to dissipate the ratio of whole to major segment.It can be pronounced,M + m = M = Φm mThus, it is safe to assumeΦ2 – Φ – 1 = 0;
Since The Phidias number Φ must be positive, thereby an equation which has a positive and a negative root
Protocols
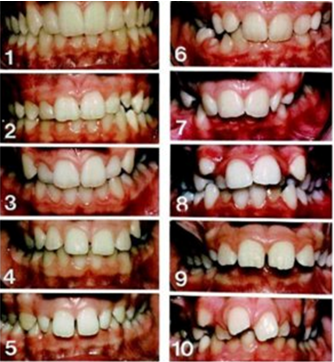
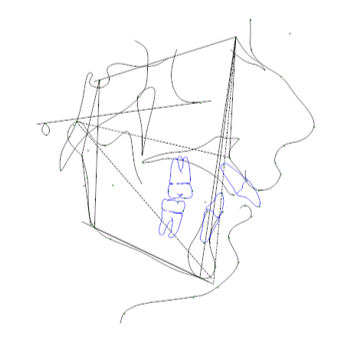
Firstly, all subjects are randomly selected from database of Department of Orthodontics & Dentofacial Orthopaedics. All subjects have to be screened for IOTN (Aesthetic Index) 11 to determine the need for Orthodontic treatment according to the severity. Once this set up is done, all subjects are distributed and arranged in different groups according to skeletal dysplasia and growth pattern. We determine craniofacial morphological parameters as described by Ricketts8 on Lateral Cephalogram and then to determine the extent to which craniofacial parameters do alter in comparison with the golden ratio.
The pre-treatment records need to be uploaded in dolphin imaging software 2D (version 11.8). Lateral Cephalogram of all subjects will be digitized & measurement will be notified in study performa.
Table 1
The characteristics are
Figure 2
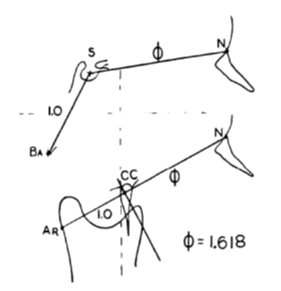
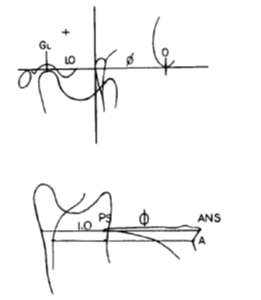
There are 9 craniofacial parameters, which are associated with Golden proportion in ideal human face.
Discussion
Cephalometric, a science that relates to measurement of face & head is rather the centuries-old and owes its development to anthropologists, anatomists, maxillofacial surgeons and orthodontists. The said facial analysis is the quantitative evaluation of all craniofacial features as specifically determined and intervened by certain norms & parameters.
EDWARD A. LUSTER’MAN (1963)10 had said since the evaluation of race types may have a profound influence on an orthodontist’s treatment planning, it must be considered one of the orthodontist’s most important diagnostic criteria. Anthropological typing of a great majority of occidental white persons in North America is fairly easy. Apart from the head form (cranial index), Face form, nose form, stature, body build, eye color, and hair texture were found to be the most highly useful criteria, although all eleven characteristics were used in this study. Because of the prevalent use of hair dyes, depilatories, etc., criteria with respect to hair had to be critically evaluated.
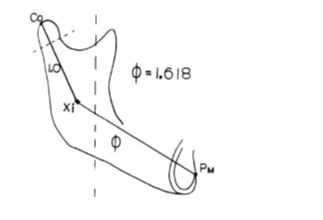
A method for finding the Arcial growth of the mandible is explained by Robert M Rickets (1972),11 along with the enumeration of some of the uses of the principle. The article also explores necessary changes in the present clinical concepts by the application of the same biological principle. According to the principle, a curve or arc at the ramus which is a segment from a circle, is followed during growth of normal human mandible; the radius of this circle is determined using distance from a point at the forking of the stress lines at the terminus of the oblique ridge on the medial side of the ramus (point Eva) to mental protuberance (Pm).
Robert M. Ricketts (1982)8, 10, 11, 9 suggested that the attraction at the limbic level in the human mind, functions in proportion to golden section. The article presents the application of basic mathematical and geometric principles to the normal morphology of structures regularly involved in orthodontics and dentistry. Models of teeth of normal occlusion subjects, photographs of the faces of commercial models, and lateral and frontal Cephalometric head films were utilized to conduct the study. The study concludes that esthetics can indeed be made scientific rather than resorting to historical subjective perceptions.
This article is neither a clinical reference nor it intends to be a debate on the facial architecture. Rather, it is a working set of facial analysis for both sexes, is presented, which for the purpose of standardization protocols and then it needs to be evolved statistically.